
FX Trading – How to Invest in Forex CFDs
In this article you will learn:
- The importance of the FX market
- Factors affecting the FX market
- How to trade in the FX market
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex, FX, or currency market, is of great importance for the global economy. Not only does it impact the financial markets, but it is also crucial for the real economy. Therefore, it is worth bearing in mind that even investors who do not invest in the forex market are, in a sense, a part of it. This is because currencies are used to conduct all transactions in different markets. For example, if investors want to buy shares, they buy them for a given currency (e.g. USD), but if traders want to buy gold, they also use a given currency (e.g. USD) and it is the same for the FX market. When you trade in the forex market, you buy or sell in currency pairs. The key to successful forex investments is to research the market properly and buy currencies that have better prospects than those whose outlook is worse.
How do foreign exchange rates work?
Currency exchange rates are fluctuating all the time for a variety of factors, for example the strength of a country’s economy. What forex traders seek to do is profit on these fluctuations by speculating whether prices will rise or fall. All forex pairs are quoted in terms of one currency versus another. Each currency pair has a ‘base’, which is the first denoted currency, and a ‘counter’, which is the second denoted currency.

Each currency could strengthen (appreciate) or weaken (depreciate). As there are two currencies in each pair, there are essentially four variables you are speculating on when it comes to forex trading.
- If you believe the value of a currency will rise against another, you go long or ‘buy’ that currency.
- If you believe the value of a currency will fall against another, you go short or ‘sell’ that currency.
So for example, if you felt the EUR would strengthen (appreciate) against the USD, you’d go long or buy the EUR/USD forex pair. You’d also buy if you felt the USD would weaken (depreciate) against the EUR.
Alternatively, if you felt the USD would strengthen against the EUR or the EUR would weaken against the USD, you’d sell or go short EUR/USD.
Because of all these factors, the forex market gives you endless possibilities every day, hour, even on a minute-to-minute basis.
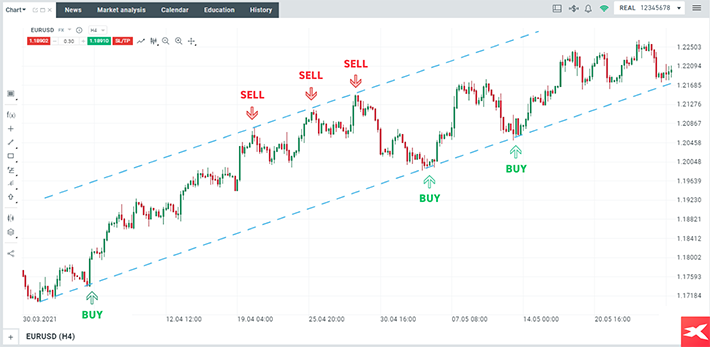
In this example, a trader could go long on EURUSD once the main currency pair bounced off the lower limit in an upward channel. Alternatively, a trader could go short on EURUSD once the pair tested the upper limit in an upward channel. Source: xStation 5
Please be aware that the presented data refers to the past performance data and such is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Factors affecting the FX market
What are some of the most important factors affecting currency exchange rates, then? First of all, the world of currencies is dominated by fundamental factors, particularly from the long-term perspective. Therefore, the strength of a certain economy determines the exchange rate of a local currency. Investors pay attention to macroeconomic releases and try to interpret the incoming data – this helps them assess the perspectives for a given currency. Most crucial economic prints include:
- Gross domestic product (GDP)
- Industrial production
- Retail sales
- Employment data
- Inflation rate
- Current account
- Survey data e.g. PMI or ISM
Moreover, currency exchange rates tend to move depending on monetary conditions. As a result, FX investors pay a lot of attention to major central banks, since these institutions are responsible for conducting monetary policy. Most notable events obviously include interest rate decisions, as higher rates generally lead to currency appreciation. In reality, there is much more to focus on, for instance, central bankers’ speeches or various reports on monetary conditions and financial stability.
Apart from fundamentals, FX traders use technical analysis while making their investment decisions. They are trying to project potential price fluctuations by studying charts – observing historical price patterns and indicators helps them assess potentially the best entry or exit points. For this reason, it is crucial to know at least some basics in terms of support or resistance levels, trading channels and trend lines.
Trading Forex CFDs
CFDs, or Contracts For Difference, are financial instruments that are a type of contract between two parties that undertake to exchange an amount whose value is equal to the difference between the opening price and the closing price of the position. CFDs are a type of over-the-counter derivative instruments. Over-the-counter because the transactions are made directly between the parties, and derivatives because their price depends on the prices of the underlying asset.
It is worth emphasising that when buying a contract for the increase of e.g. EUR / USD or gold, we do not actually purchase currency or precious metal and we do not become their owner.
Contracts for currencies (forex) are one of the most frequently used individual financial instruments by investors for a reason. Their popularity is due to a set of specific features of currency CFD trading:
- Trading hours – it is said that the Forex market does not sleep because trading on it is possible 24 hours a day, from Monday to Friday!
- Easy availability – usually investments are associated with a large expenditure of funds (the so-called high entry threshold), while to start trading on the Forex market, you generally require a lower amount of pounds, dollars or euros, and no minimum deposit is needed.
- Leverage – Forex CFDs (like most derivatives) have a built-in leverage. This means that you only need a percentage of the full investment value to open a position. For example, an investment in EUR / USD worth 10,000 euros requires a security deposit of 333 euros. You should also bear in mind that due to the leverage, both the potential profits and the size of the possible loss are increased.
- Low trading costs – with most Forex brokers, opening and maintaining an account is free, and commissions for buying and selling CFDs are counted in thousandths of a percent. The cost of opening an order in the forex market may be, depending on the type of account, a spread or a spread and commission.
- Trading for ups and downs – unlike many “classic” forms of investment (e.g. buying stocks on the stock exchange) using CFDs on currencies, you can speculate on the forex market whether the price of a given currency pair will rise or fall. If we play “for an increase” in the price of a given asset, it means that we open a long position, and by playing for a “decline” we open a short position.
- High volatility – speculation is based on a very simple assumption – it is about buying (or selling) something at a favorable price and then selling (or buying back) at a better price. Therefore, for speculators, volatility is a very important factor determining the attractiveness of a given market, and the Forex market is one of the most volatile markets in the world. However, higher volatility might also be seen as a two-edged sword, which means that the size of both potential profits and losses may be much bigger.
Examples of FX trading
Example 1 – GBPUSD
Let’s imagine that the United Kingdom released employment data. The publication turned out to be worse-than-expected as employment fell while the consensus estimate suggested an increase. Therefore, the unemployment rate rose unexpectedly. In theory, such a situation could potentially be negative for the British pound (GBP) amid concerns of economic growth. In such a scenario, some traders may decide to bet against the GBP shortly after the release, for instance, by going short on the GBPUSD CFD pair.
In order to open a short position, a trader should choose an appropriate volume and click the red button that may be found in the upper-left corner of the chart – an instant execution is the quickest way to place any trade. The red button always shows a price at which you can enter a short position.

In order to short a currency pair, you can click the red button, which represents selling the currency pair (the area marked with an arrow is a built-in “Click & Trade” module). Obviously you do not need to own any underlying instrument while trading CFDs. Source: xStation5
Please be aware that the presented data refers to the past performance data and such is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Example 2 – AUDUSD
Let’s imagine that the Reserve Bank of Australia decided to start tightening its policy and raised its interest rates. As it was already explained above, such measures may contribute to currency appreciation – higher rates increase the value of that country’s currency.
As a result, a trader may decide to open a long position on the Australian dollar after the RBA’s policy announcement, for example, by going long on the AUDUSD CFD.
Traders are able to open long positions directly through the “Market Watch” tab in the xStation 5 platform. In order to do that, you should just click the “buy” button. Alternatively, you can bet against other currencies by clicking the “sell” button. These positions work exactly in the same way, meaning that you are able to bet on both appreciation and depreciation of various currencies.
Please be aware that the presented data refers to the past performance data and such is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Example 3 – USDTRY
Now let’s touch on some emerging markets currency, namely the Turkish lira (TRY). Let’s assume that a trader decides to short the currency due to political factors (like the government’s interference into monetary policy). In this case, a trader may decide for the USDTRY CFD pair and go long, betting that the TRY will weaken against the USD – and vice versa – the USD will strengthen against the TRY.

In order to go long, you can click the “buy” button, thus placing an order. Source: xStation5
Please be aware that the presented data refers to the past performance data and such is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Summary
To summarise, the FX market gives investors plenty of opportunities, as they can go either long or short – the variety of currency pairs makes it even more compelling. If you expect a certain currency to advance, you can always place an appropriate trade in a given currency pair. The same goes for shorting currencies – you can place a trade that would become profitable once the currency depreciates. The choice is up to you, as you do not need to own the asset to trade on price declines!
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 77% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
This material is a marketing communication within the meaning of Art. 24 (3) of Directive 2014/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 May 2014 on markets in financial instruments and amending Directive 2002/92/EC and Directive 2011/61/EU (MiFID II). Marketing communication is not an investment recommendation or information recommending or suggesting an investment strategy within the meaning of Regulation (EU) No 596/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 April 2014 on market abuse (market abuse regulation) and repealing Directive 2003/6/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Directives 2003/124/EC, 2003/125/EC and 2004/72/EC and Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/958 of 9 March 2016 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 596/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to regulatory technical standards for the technical arrangements for objective presentation of investment recommendations or other information recommending or suggesting an investment strategy and for disclosure of particular interests or indications of conflicts of interest or any other advice, including in the area of investment advisory.
The marketing communication is prepared with the highest diligence, objectivity, presents the facts known to the author on the date of preparation and is devoid of any evaluation elements. The marketing communication is prepared without considering the client’s needs, his individual financial situation and does not present any investment strategy in any way. The marketing communication does not constitute an offer of sale, offering, subscription, invitation to purchase, advertisement or promotion of any financial instruments.
X-Trade Brokers Dom Maklerski S.A. is not liable for any client’s actions or omissions, in particular for the acquisition or disposal of financial instruments, undertaken on the basis of the information contained in this marketing communication.
In the event that the marketing communication contains any information about any results regarding the financial instruments indicated therein, these do not constitute any guarantee or forecast regarding the future results.
